In a recent benchmark, Diffbot placed first overall among text extraction APIs on an academic evaluation set and one sampled from Google News.
Tomaz Kovacic, a university student in artificial intelligence, recently conducted a comprehensive benchmark of text extraction methods as part of his thesis. Included in the study are commercial vendors as well as open-source APIs for text extraction. He did an excellent job in designing the study, measuring both precision, recall, F1, as well as careful error case analysis.
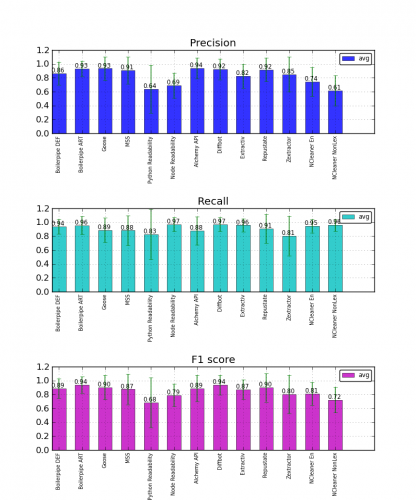
The CleanEval dataset, developed at the Association of Computational Linguistics conference, is a widely used evaluation in academia, and the Google News article dataset was sampled from the 5000+ news sources that Google aggregates.
Diffbot’s method relies on training a core set of visual features (such as geometrical, stylistic, and render properties) to recognize different types of documents. In this case, we had trained Diffbot on a set of news article typed pages to recognize certain parts of news pages. In addition to article text, Diffbot’s article API returns the content author, date, location, article images, article videos, favicon, and even topics (support in English and other languages coming soon). Besides article pages, Diffbot’s core features have been trained to extract information from other types of pages too (such as frontpages).
This result gives us great promise that generalized vision-based machine learning techniques can perform just as well, if not better, than approaches engineered for specific tasks.
Learn more details about the study.
You must be logged in to post a comment.